Ray Use Cases#
This page indexes common Ray use cases for scaling ML. It contains highlighted references to blogs, examples, and tutorials also located elsewhere in the Ray documentation.
LLMs and Gen AI#
Large language models (LLMs) and generative AI are rapidly changing industries, and demand compute at an astonishing pace. Ray provides a distributed compute framework for scaling these models, allowing developers to train and deploy models faster and more efficiently. With specialized libraries for data streaming, training, fine-tuning, hyperparameter tuning, and serving, Ray simplifies the process of developing and deploying large-scale AI models.
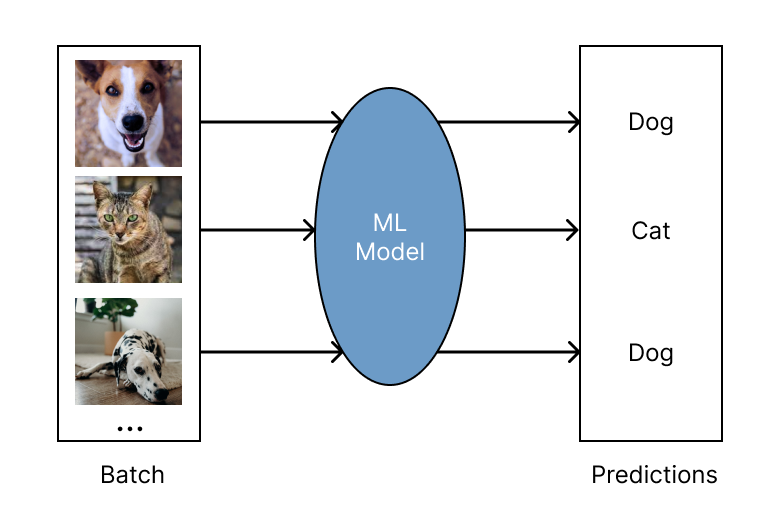
Batch Inference#
Batch inference is the process of generating model predictions on a large “batch” of input data. Ray for batch inference works with any cloud provider and ML framework, and is fast and cheap for modern deep learning applications. It scales from single machines to large clusters with minimal code changes. As a Python-first framework, you can easily express and interactively develop your inference workloads in Ray. To learn more about running batch inference with Ray, see the batch inference guide.
Model Serving#
Ray Serve is well suited for model composition, enabling you to build a complex inference service consisting of multiple ML models and business logic all in Python code.
It supports complex model deployment patterns requiring the orchestration of multiple Ray actors, where different actors provide inference for different models. Serve handles both batch and online inference and can scale to thousands of models in production.
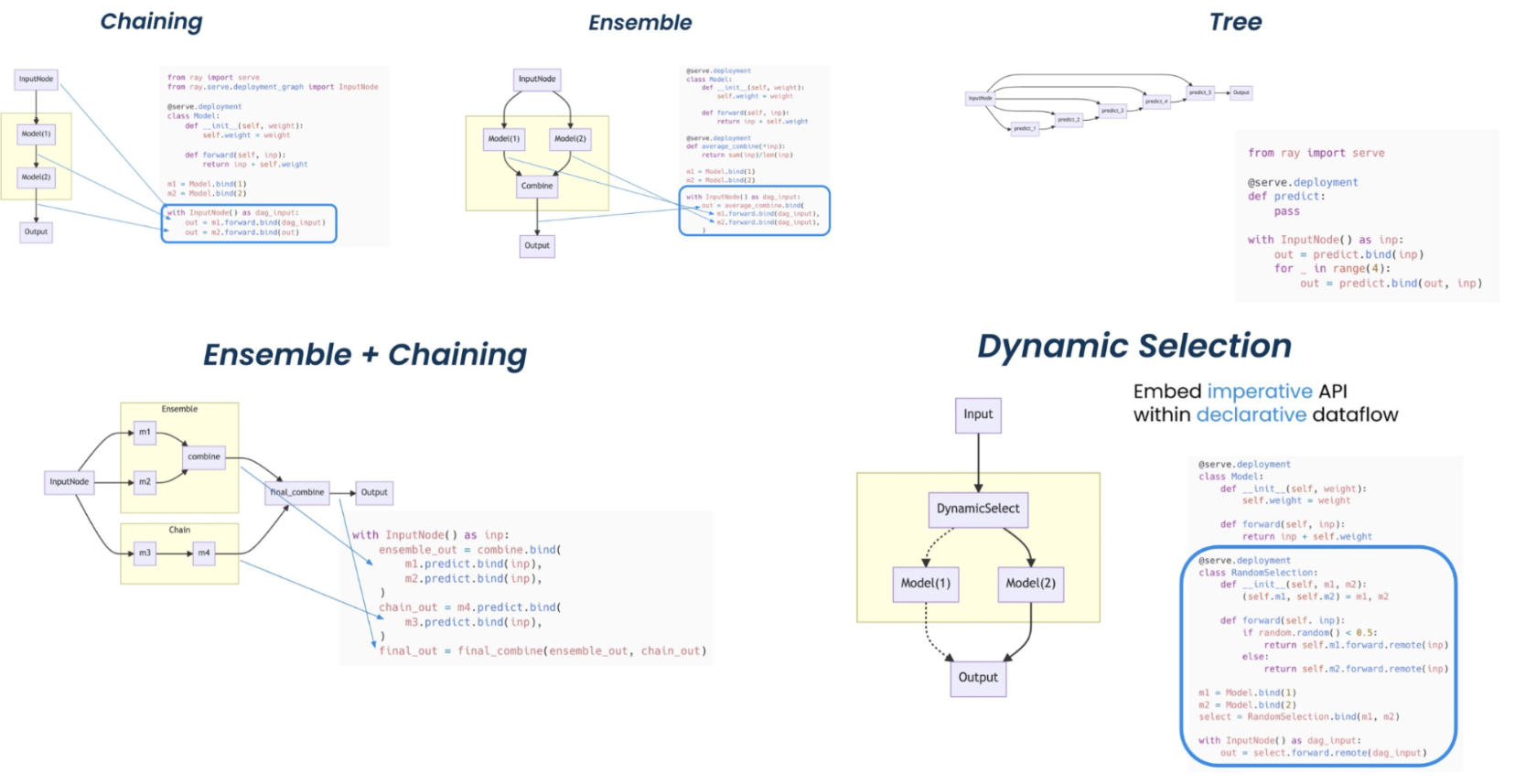
Deployment patterns with Ray Serve. (Click image to enlarge.)#
Learn more about model serving with the following resources.
Hyperparameter Tuning#
The Ray Tune library enables any parallel Ray workload to be run under a hyperparameter tuning algorithm.
Running multiple hyperparameter tuning experiments is a pattern apt for distributed computing because each experiment is independent of one another. Ray Tune handles the hard bit of distributing hyperparameter optimization and makes available key features such as checkpointing the best result, optimizing scheduling, and specifying search patterns.
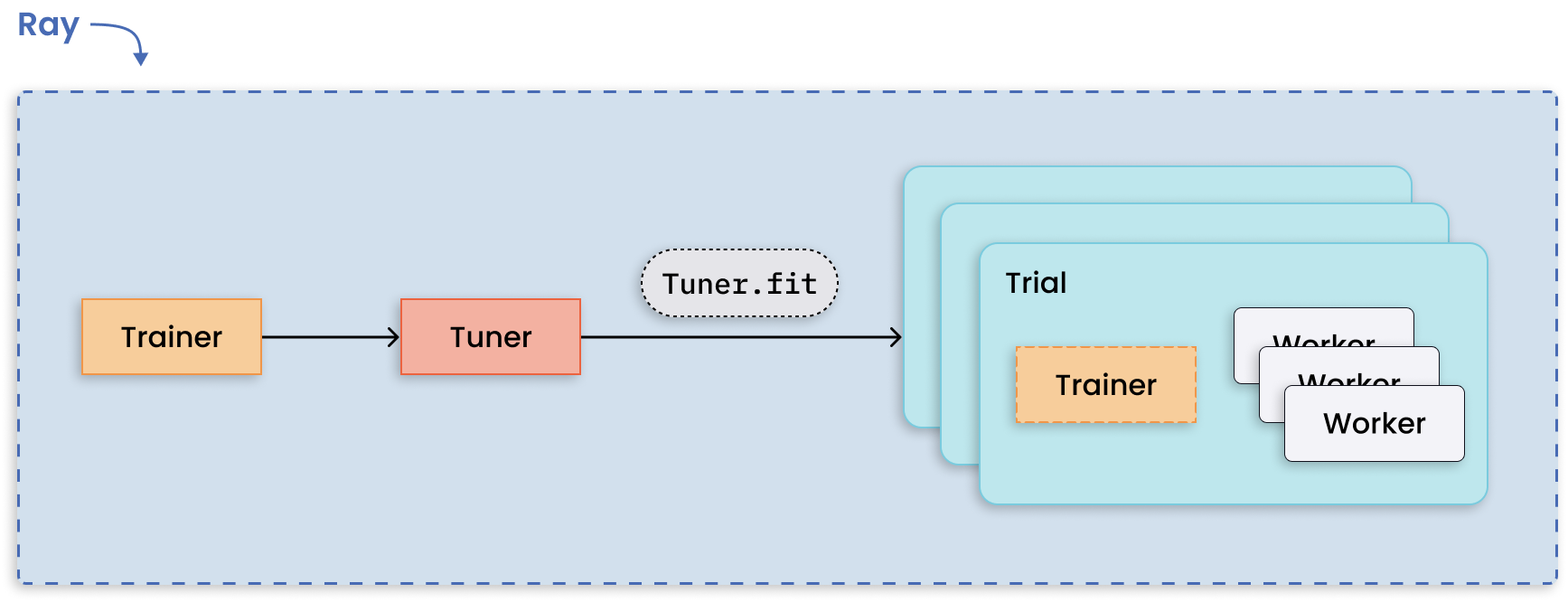
Distributed tuning with distributed training per trial.#
Learn more about the Tune library with the following talks and user guides.
Distributed Training#
The Ray Train library integrates many distributed training frameworks under a simple Trainer API, providing distributed orchestration and management capabilities out of the box.
In contrast to training many models, model parallelism partitions a large model across many machines for training. Ray Train has built-in abstractions for distributing shards of models and running training in parallel.
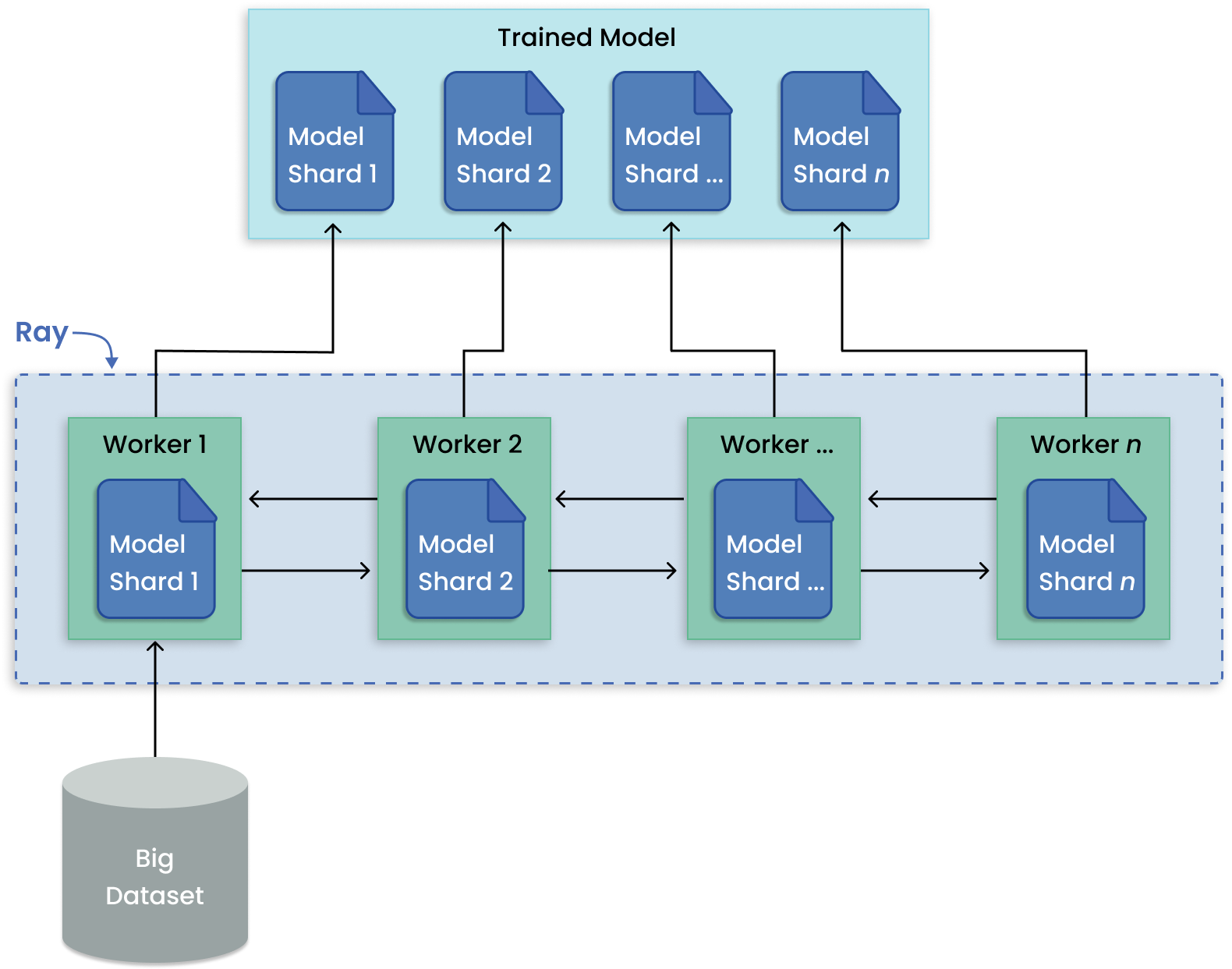
Model parallelism pattern for distributed large model training.#
Learn more about the Train library with the following talks and user guides.
Reinforcement Learning#
RLlib is an open-source library for reinforcement learning (RL), offering support for production-level, highly distributed RL workloads while maintaining unified and simple APIs for a large variety of industry applications. RLlib is used by industry leaders in many different verticals, such as climate control, industrial control, manufacturing and logistics, finance, gaming, automobile, robotics, boat design, and many others.
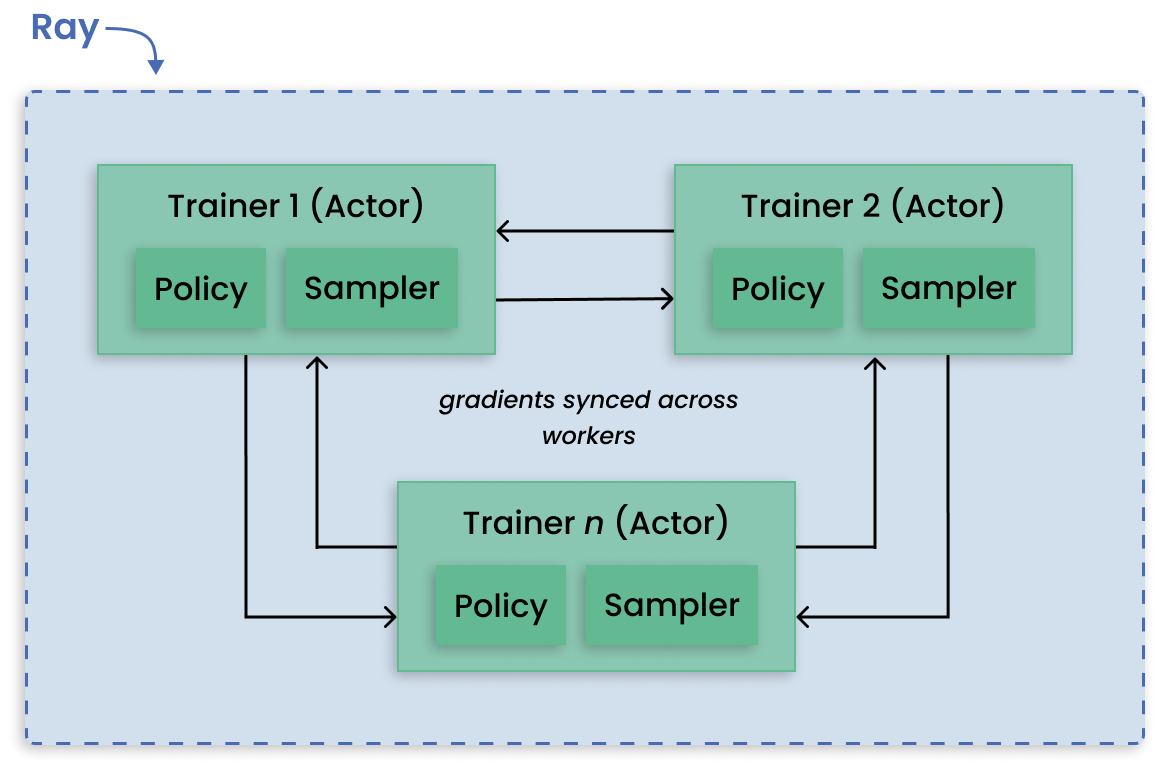
Decentralized distributed proximal policy optimization (DD-PPO) architecture.#
Learn more about reinforcement learning with the following resources.
ML Platform#
Ray and its AI libraries provide unified compute runtime for teams looking to simplify their ML platform. Ray’s libraries such as Ray Train, Ray Data, and Ray Serve can be used to compose end-to-end ML workflows, providing features and APIs for data preprocessing as part of training, and transitioning from training to serving.
Read more about building ML platforms with Ray in this section.
End-to-End ML Workflows#
The following highlights examples utilizing Ray AI libraries to implement end-to-end ML workflows.
Large Scale Workload Orchestration#
The following highlights feature projects leveraging Ray Core’s distributed APIs to simplify the orchestration of large scale workloads.